First Class Tips About Is AC Both Positive And Negative
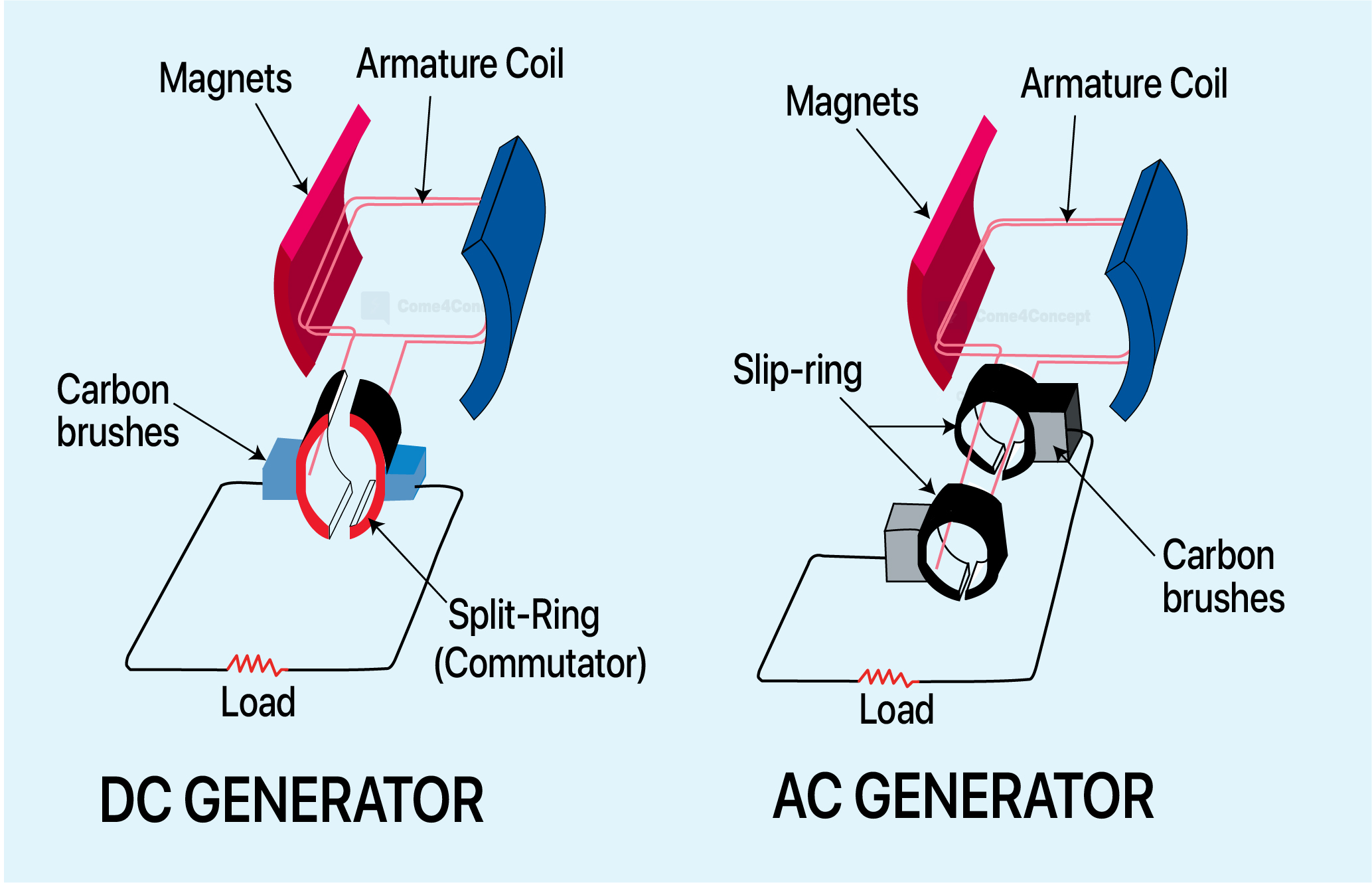
Simple Diagram Of Ac Generator
AC
1. Understanding Alternating Current
Ever wondered about that cool breeze coming from your air conditioner? Or perhaps you've pondered the electricity powering your devices? The answer often lies in AC, or Alternating Current. Unlike DC (Direct Current) which flows in one direction, AC is a bit of a rebel; it changes direction periodically. Now, that brings us to the intriguing question: is AC both positive and negative? Let's dive in, and I promise, it's less complicated than assembling IKEA furniture.
Think of AC as a swing set. It doesn't just go forward, it swings back and forth. This constant change in direction is what gives AC its unique characteristics. This "swinging" is described in terms of a wave, oscillating between a positive peak and a negative trough. This oscillation is fundamental to how AC delivers power to our homes and businesses.
The crucial thing to remember is that the voltage in an AC circuit doesn't just stay at a constant positive value. It varies in a sinusoidal pattern, dipping into negative values before returning to positive again. This continuous shift is the very essence of alternating current. It's like a never-ending dance of electrons, and that's what allows it to travel long distances efficiently.
So, to directly address the question, yes, AC voltage and current are indeed both positive and negative as they cycle through their alternating pattern. This makes it uniquely suited for powering a wide variety of devices, from your phone charger to the giant machines in factories. It is one the most common electrical flow in the world.

Opposite Charges Attract
The Sine Wave
2. Decoding the Wave
Alright, let's picture this whole positive-negative thing. Imagine a smooth, rolling wave. This is what a graph of AC voltage looks like over time — a sine wave. The top part of the wave represents the positive voltage, while the bottom part represents the negative voltage. The wave crosses the zero line in between, signifying that at that instant, the voltage is neither positive nor negative.
This sine wave isn't just a pretty picture; it tells us a lot about the AC power. The height of the wave (amplitude) represents the peak voltage, and the number of times the wave repeats itself per second is the frequency (measured in Hertz). In the US, that's typically 60 Hz, meaning the voltage switches direction 60 times every second! That's a fast dance!
Now, don't let the negative voltage freak you out. It doesn't mean your appliances are getting "negative" power. It simply means the electrons are flowing in the opposite direction compared to when the voltage is positive. Your appliances don't care which direction the electrons are flowing; they just need the energy to do their thing.
Understanding the sine wave helps to illustrate that AC voltage is not a constant value; its a dynamic, ever-changing quantity that fluctuates between positive and negative extremes. This is what makes AC so versatile and effective for transmitting power over long distances, and this is something that made this article exist in the first place.

Why the Alternation Matters
3. The Advantages of AC
So, why bother with all this alternating business? Why not just stick with DC? Well, AC has some serious advantages, primarily when it comes to transmitting power over long distances. One major factor is the ease with which AC voltage can be stepped up or down using transformers.
Think about it: Power companies need to send electricity from power plants to our homes, which can be hundreds of miles away. Transmitting power at high voltage reduces energy loss due to resistance in the wires. AC transformers make it simple to increase the voltage for transmission and then decrease it again to safe levels for use in our homes.
Trying to do the same with DC is much more complicated and inefficient. This is why AC became the dominant form of power distribution early in the history of electrification. So, the next time you flip a light switch, remember that you're benefiting from the clever properties of alternating current.
Furthermore, AC allows for the use of induction motors, which are generally simpler, cheaper, and more reliable than DC motors. These motors are workhorses in countless appliances and industrial applications. All this flexibility and efficiency adds up to significant cost savings and makes AC a truly invaluable tool.

Sinusoidal Waveforms Or Sine Wave In An AC Circuit
AC and Safety
4. Respect the Power
Now, a word of caution: electricity, whether AC or DC, should always be treated with respect. Because AC voltage oscillates, there are additional hazards to be mindful of. While the constant changes in direction dont necessarily make it more dangerous than DC, understanding how AC behaves is key to staying safe.
One potential danger with AC is its effect on the human body. The alternating current can cause muscles to contract involuntarily, making it difficult to let go of a live wire. This is why electrical safety is so critical. Always follow safety guidelines when working with electricity, and never take risks.
Make sure your home's wiring is up to code, and that you have proper grounding and circuit breakers to protect against electrical shocks and fires. Remember, electricity is a powerful force, and a little knowledge can go a long way in keeping you and your loved ones safe. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, always call a qualified electrician.
In summary, while the back-and-forth nature of AC brings many benefits, safety should always be your number one priority when dealing with electrical systems. Treat AC with the respect it deserves, and it will continue to power our lives safely and effectively.

AC in Everyday Life
5. Ubiquitous AC
We've talked about how AC powers our homes, but its influence extends far beyond the wall socket. Think about the many electronic devices we use every day — computers, televisions, smartphones, and countless others. While these devices often use DC internally, they rely on AC power from the grid to function.
Your computer's power supply, for example, converts the AC voltage from the wall into the DC voltage that the computer's components need. This conversion process is essential for the operation of nearly all modern electronics. So, even if you think you're living in a DC world, AC is still working behind the scenes.
AC is also vital in many industrial processes, powering heavy machinery, driving pumps and compressors, and enabling a wide range of manufacturing operations. It's the backbone of our modern industrial economy, quietly powering the world around us. It is also very important in various types of electronics, powering big and small electrical components.
From the lights in our homes to the massive machines in factories, AC plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Understanding its properties, including its oscillating positive and negative voltages, helps us appreciate the ingenuity and importance of this fundamental form of electrical power. It is something that we should be aware of.

Positive And Negative Wiring Colors
FAQ
6. Your AC Questions Answered
Q: Is AC more dangerous than DC?A: Not necessarily. Both AC and DC can be dangerous if handled improperly. The effect of AC on the human body can cause muscles to contract, making it difficult to let go of a live wire. However, DC can also cause severe burns. The most important thing is to understand the risks and follow proper safety precautions regardless of the type of current.
Q: Can I convert AC to DC?A: Absolutely! This is what devices like phone chargers and computer power supplies do. They use a rectifier to convert AC voltage into DC voltage suitable for the device's internal components. This process is very common in modern electronics.
Q: What does Hertz (Hz) mean in AC power?A: Hertz (Hz) is the unit of frequency, which tells you how many times the AC voltage cycles between positive and negative per second. In the United States, the standard frequency is 60 Hz, meaning the voltage switches direction 60 times every second.