Marvelous Tips About How To Generate 3 Phase AC From Single-phase
How To Convert 3Phase AC Single Phase
Turning Single-Phase into a Three-Phase Powerhouse
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered how those massive industrial machines hum along so smoothly? A big part of it is three-phase AC power. But what if you only have single-phase available? Don't fret! While it might seem like trying to turn water into wine, generating three-phase AC from a single-phase source is entirely possible. It's not magic, just some clever electrical engineering principles at play. Think of it like this: you're taking one stream of water and splitting it into three, but making sure they're all flowing at slightly different times. That's the core idea behind phase conversion.
Now, you might be asking, why bother? Well, three-phase power delivers power more efficiently and smoothly than single-phase, especially for large motors and other demanding equipment. Imagine trying to row a boat with one oar versus three — which would be smoother and more powerful? Exactly! Thats the advantage of three-phase.
So, whether you're a hobbyist tinkering in your workshop, an engineer designing industrial systems, or simply curious about the wonders of electricity, understanding how to convert single-phase to three-phase is a valuable piece of knowledge. We'll break down the common methods, demystify the jargon, and hopefully, even make you chuckle along the way.
Before we dive in, let's quickly recap the difference. Single-phase AC power, like what you have in your home outlets, delivers power in a pulsating way, like a heartbeat. Three-phase, on the other hand, is like a smooth, constant flow. It provides more consistent torque in motors and handles heavy loads with much more grace. Its the preferred choice for many industrial applications.

The Rotary Phase Converter
2. How it Works
One popular way to generate three-phase from single-phase is using a rotary phase converter. This device is essentially a three-phase motor that's specially designed to run on single-phase power. Sounds a bit counterintuitive, right? But heres the catch: this motor is not used to drive anything directly. Instead, it acts as a sort of "phase generator," creating the missing phases needed for a three-phase system. It's like a translator that takes single-phase and spits out three-phase.
Inside the rotary phase converter, the single-phase power is used to spin the motor. As the motor spins, it generates voltage on the other two phases, creating a balanced three-phase output. Think of it like a record player: the single-phase power is the needle that gets the platter spinning, and as the platter spins, it creates the music (the three-phase power). Of course, it's a bit more complicated than that, involving capacitors and carefully designed windings to ensure the output is stable and balanced, but that's the basic principle.
Rotary phase converters are great for running multiple three-phase motors simultaneously, making them a common choice for workshops and small businesses. They're also relatively robust and can handle varying loads pretty well. However, they do require a bit of maintenance and tend to be a bit noisier than other types of converters. So, if you value peace and quiet, you might want to consider another option. But if you need reliable three-phase power for your machines, a rotary converter is a solid choice.
They also come in various sizes, so you can choose one that matches your power requirements. It's important to select the right size converter to avoid overloading it and potentially damaging your equipment. Always consult with an electrician or qualified professional to ensure you're making the right choice. And remember, safety first! Working with electricity can be dangerous, so always take the necessary precautions.

Static Phase Converters
3. Simplicity in Design
If a rotary converter sounds a bit too complex, a static phase converter might be more your speed. These converters are simpler in design and generally smaller than rotary converters. They achieve phase conversion using capacitors and reactors to create a pseudo third phase. Unlike rotary converters, static converters don't actually spin anything. That means they're quieter and require less maintenance.
However, there's a trade-off. Static phase converters typically provide less starting torque for motors than rotary converters. This means they may not be suitable for applications that require high starting torque, such as compressors or certain types of pumps. Think of it like trying to start a car in too high a gear — it's going to struggle. But for less demanding applications, like running a lathe or a mill, a static converter can be a cost-effective and space-saving solution.
The way a static converter creates a pseudo third phase is by using capacitors to shift the phase angle of the single-phase input. This creates a voltage that is out of phase with the original input, effectively simulating a three-phase system. However, because it's just a simulation, the resulting three-phase power is not as balanced or as stable as that from a rotary converter. Thats why they're typically used for lighter loads and less demanding applications.
One key advantage of static phase converters is their lower cost. They are often a more affordable option for hobbyists or small businesses that only need to run a single three-phase motor occasionally. Just make sure to check the motor's starting torque requirements before choosing a static converter. You don't want to end up with a converter that can't handle the job! And, as always, consult with a qualified electrician to ensure the converter is properly installed and safe to use.
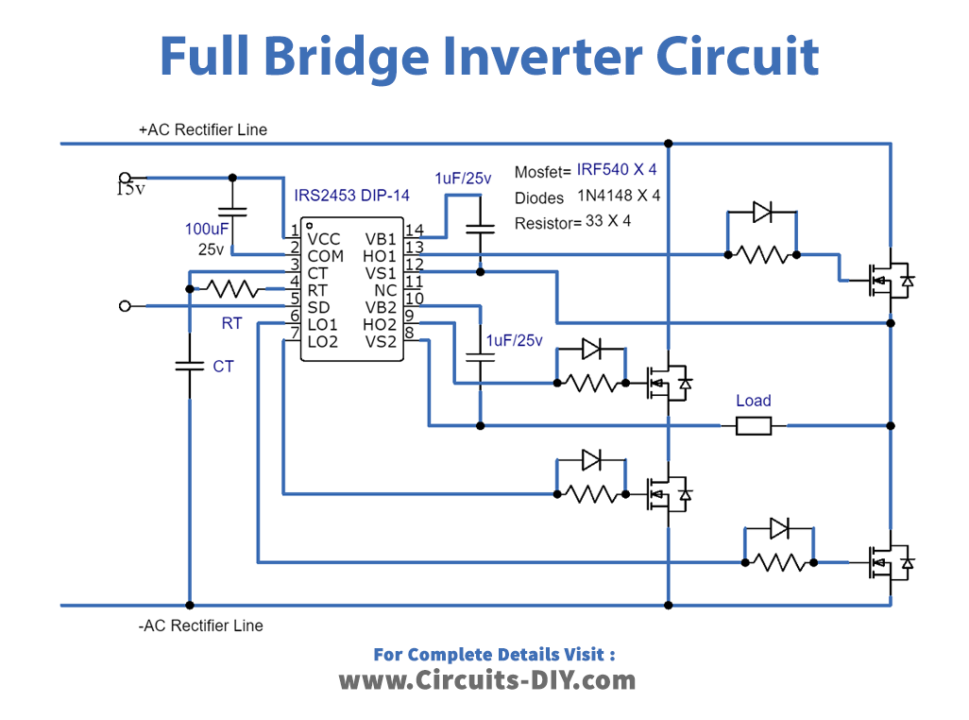
What Is 3 Phase Converter? Types, Working & Circuit Diagram
VFDs
4. Variable Frequency Drives
For the ultimate in control and efficiency, consider using a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD). While VFDs are primarily designed to control the speed of AC motors, they also have the ability to convert single-phase AC to three-phase AC. This makes them a versatile solution for a wide range of applications, from controlling HVAC systems to running industrial machinery.
VFDs work by first converting the incoming single-phase AC power into DC power. Then, using sophisticated electronic circuitry, they convert the DC power back into three-phase AC power with the desired frequency and voltage. This allows you to not only convert the phase but also precisely control the speed and torque of the motor, leading to significant energy savings and improved performance. It's like having a super-smart electrical brain that can adjust the power to exactly what the motor needs, when it needs it.
VFDs are more expensive than rotary or static phase converters, but they offer a number of advantages that can justify the investment. In addition to phase conversion and speed control, VFDs can also protect motors from overloads, undervoltage, and other electrical faults. They can also be programmed to perform complex control functions, such as maintaining constant pressure or flow rate. This makes them a popular choice for industrial automation applications. Plus, they're usually quieter than rotary converters and more efficient than static converters.
Choosing a VFD also opens doors to energy efficiency. By adjusting the motor's speed to match the load, VFDs can significantly reduce energy consumption, especially in applications with variable loads. This can lead to substantial cost savings over time. Of course, VFDs can be a bit more complex to set up and program than other types of converters, so it's important to have a good understanding of their operation or to seek assistance from a qualified technician. But once they're set up, they can provide years of reliable and efficient service.

Choosing the Right Converter for Your Needs
5. Making the Right Decision
So, which type of converter is right for you? The answer depends on several factors, including the power requirements of your equipment, your budget, the desired level of control, and the space available. Rotary phase converters are a good choice for running multiple three-phase motors simultaneously, especially if high starting torque is required. Static phase converters are a more affordable option for running a single three-phase motor with lower starting torque requirements. VFDs offer the most control and efficiency but come at a higher cost.
Consider the specific applications you'll be using the three-phase power for. If you're running a CNC machine, you'll likely need a rotary converter or a VFD to provide the necessary power and control. If you're just running a small woodworking machine, a static converter might be sufficient. Also, think about the long-term costs. While a VFD might be more expensive upfront, it can save you money on energy bills in the long run. It's a bit like buying a hybrid car — it costs more initially but saves you money on gas over time.
It's also crucial to consider the electrical safety requirements in your area. Make sure that any converter you choose is properly certified and installed by a qualified electrician. Working with electricity can be dangerous, so it's always best to err on the side of caution. And remember, a properly installed and maintained converter will provide years of reliable service, ensuring that your equipment runs smoothly and efficiently. Don't skimp on quality or safety! It's not worth the risk.
Before making a final decision, its always a good idea to consult with an electrical professional who can assess your specific needs and recommend the best solution for your situation. They can help you determine the appropriate size and type of converter, ensuring that it meets your power requirements and complies with all applicable safety regulations. They can also provide valuable advice on installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. So, dont hesitate to seek expert guidance — it could save you a lot of headaches (and potentially dangerous situations) down the road!

FAQs
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
We know you probably still have some questions swirling around. Here are a few common ones we hear, along with some hopefully helpful answers:
Q: Can I just wire my single-phase motor to a three-phase outlet?A: Absolutely not! That's a recipe for disaster (and potentially a very expensive paperweight). Single-phase and three-phase motors are designed differently and require different power supplies. Plugging a single-phase motor into a three-phase outlet will likely damage the motor (and possibly the outlet too!). Always use the correct power supply for your motor.
Q: Are phase converters noisy?A: It depends! Rotary phase converters tend to be noisier than static converters or VFDs because they have a spinning motor. Static converters are generally quieter, and VFDs are often the quietest of the three. If noise is a concern, consider a static converter or a VFD.
Q: Can I use a phase converter to power my whole house?A: While technically possible, it's generally not recommended. Phase converters are typically used to power specific three-phase equipment, not an entire household. The power demands of a whole house are much more complex and varied, and it's usually more cost-effective and efficient to stick with single-phase power for most residential applications. Plus, most household appliances are designed to run on single-phase power anyway.
Q: How do I size a phase converter correctly?A: Sizing a phase converter depends on the power requirements of the three-phase equipment you'll be running. You'll need to know the voltage, current, and horsepower (or kilowatt) ratings of the motor or equipment. Consult the converter manufacturer's specifications and guidelines to ensure you choose a converter that can handle the load. It's always better to err on the side of caution and choose a slightly larger converter than you think you need. And, as we've said before, consulting with an electrician is always a good idea!