Matchless Tips About What Is V And VA
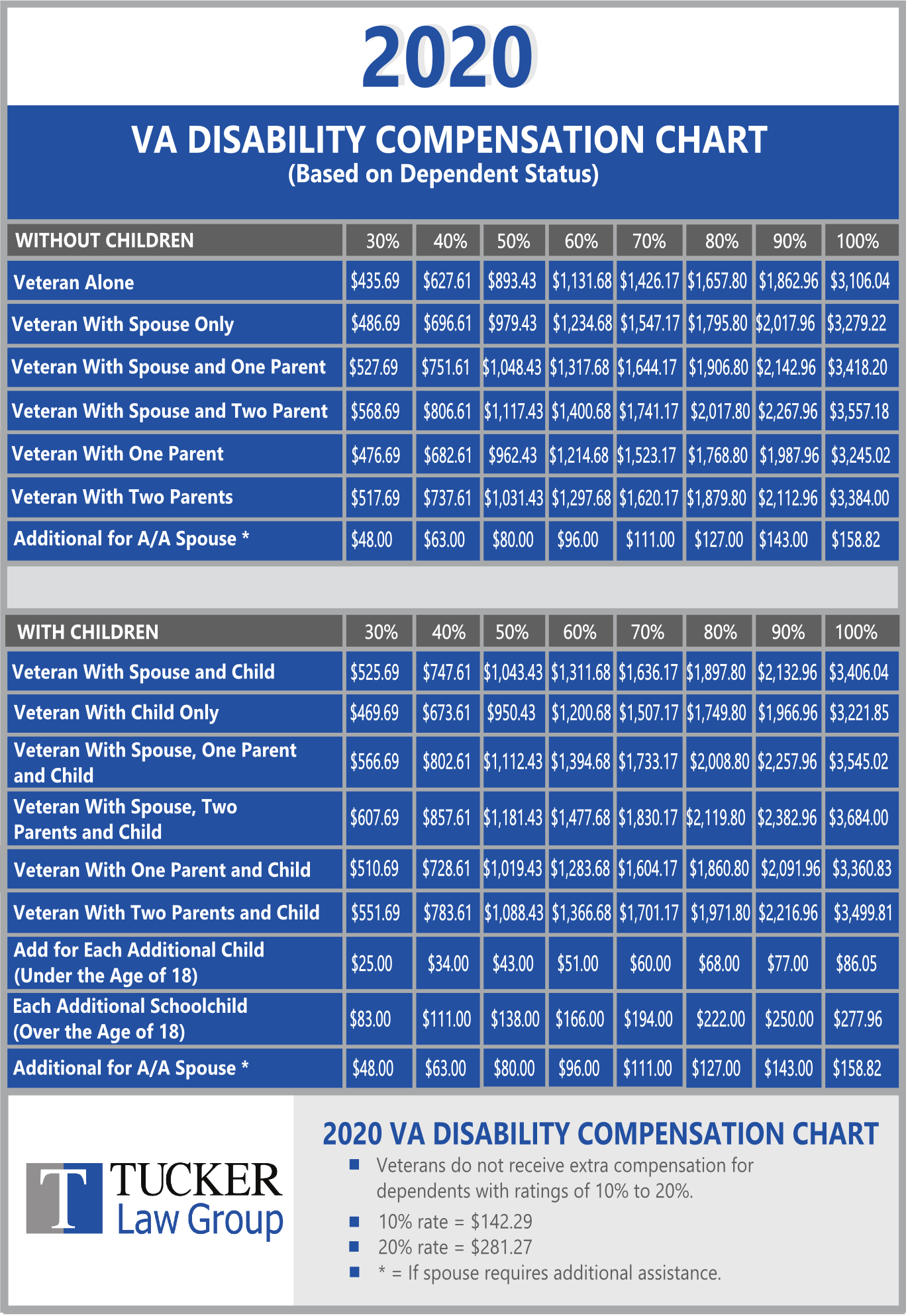
Va Compensation For 2025
Decoding V and VA
1. Unveiling the Mystery of V and VA
Alright, let's tackle this head-on: What exactly is V and VA? It sounds like something from a superhero comic, doesn't it? While it might not grant you superpowers, understanding V and VA is pretty darn useful, especially when we're talking about electrical stuff. So, buckle up, because we're diving in!
At its core, 'V' stands for Voltage. Think of it as the electrical pressure that pushes electrons through a circuit, like water pressure in a pipe. The higher the voltage, the stronger the push — and the more potential there is for things to happen (like lighting up a bulb or running a motor). Its measured in volts (naturally!).
Now, what about VA? That's Volt-Amperes. It's the measure of apparent power in an AC (alternating current) circuit. It's calculated by multiplying the voltage (V) by the current (Amperes, A). But heres the catch: its the apparent power. It doesnt always tell you how much real power is being used.
Why do we need VA then? Because in AC circuits, voltage and current aren't always perfectly in sync. This mismatch is where things get interesting (and sometimes a little confusing). VA helps us understand the total capacity a circuit needs to handle, even if some of that energy isn't being used to do actual work.

Cách Sử Dụng To V Và Ving Trong Tiếng Anh IELTS MINDX
VA Explained
2. The Power Trio
Okay, let's break down this VA concept further. Imagine you're pushing a swing. Some of your energy goes into making the swing go higher (the real power). But some energy is used just to get the swing moving back and forth (the reactive power), which doesnt contribute to lifting it higher. VA is like the total effort you put in, including both the useful and the not-so-useful parts.
Real power, measured in Watts (W), is the power that actually does work — like powering your TV or running your refrigerator. Reactive power, measured in VAR (Volt-Ampere Reactive), is the power that's stored and released in the circuit due to components like capacitors and inductors. It's essential for AC circuits to function, but it doesn't directly perform work. VA is the vector sum of real and reactive power.
Think of it like this: you're pouring a beer. The actual beer you drink is the real power (Watts). The foam is the reactive power (VAR). And the total volume you poured (beer + foam) is the apparent power (VA). You have to pour the total volume, even if you only actually drink the beer part!
Understanding this difference is crucial for designing and managing electrical systems. If you only consider the Watts (real power), you might underestimate the total current a circuit needs to handle. Overlooking VA can lead to overloaded circuits, blown fuses, and potentially even electrical fires. So, pay attention to both!
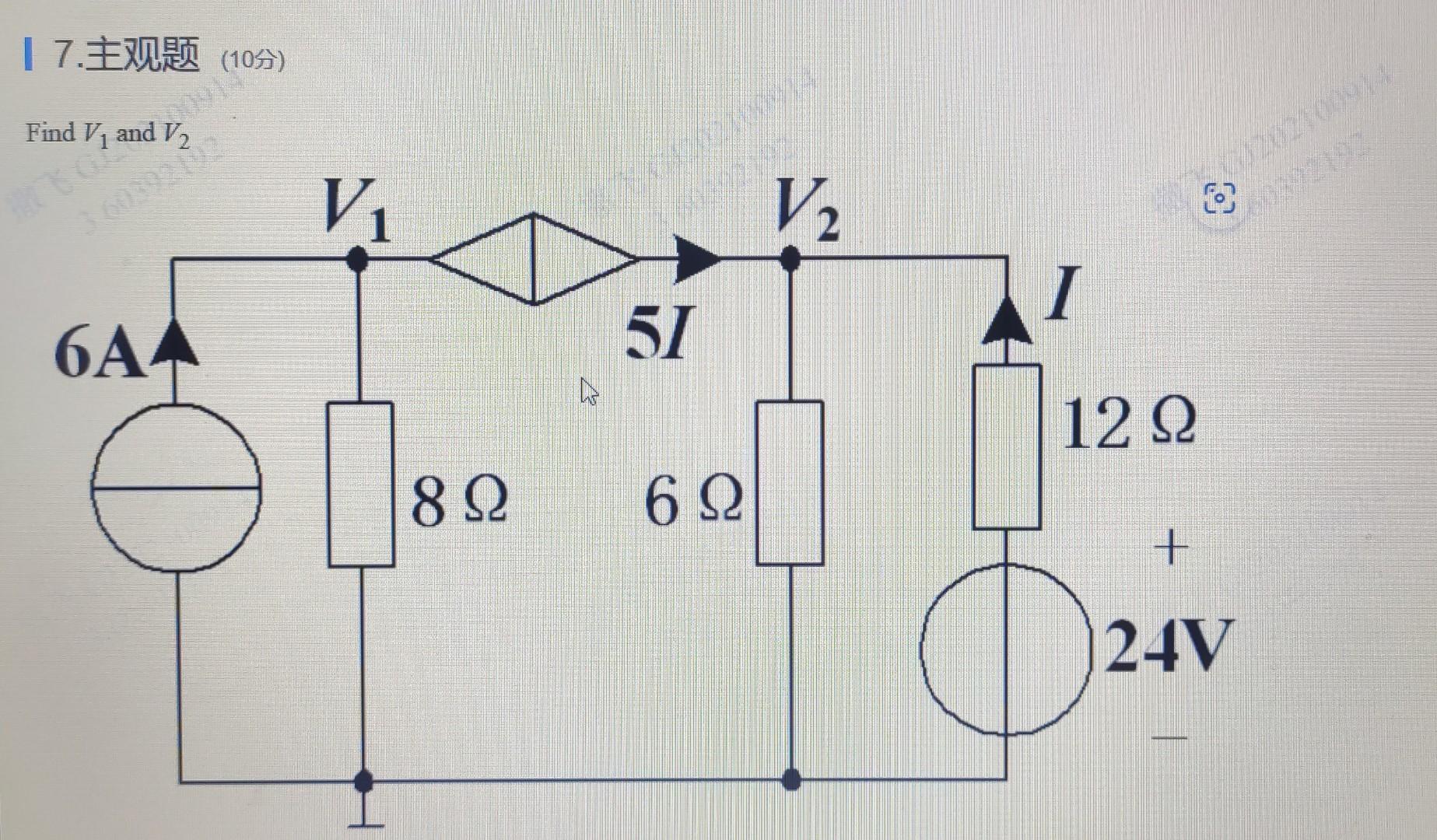
Solved Find V+and Va
Why VA Matters
3. From Power Plants to Your Phone Charger
So, where does all this VA stuff come into play in the real world? Pretty much everywhere electricity is used, actually. Lets start big: power plants. They need to know the VA rating of their generators to ensure they can handle the total load demanded by consumers. They also use power factor correction (more on that later!) to minimize reactive power and maximize efficiency.
Then there are transformers. Transformers are used to step up or step down voltage levels. Their VA rating indicates how much apparent power they can handle without overheating or failing. Choosing the right transformer VA rating is critical for ensuring reliable and safe operation of electrical equipment.
Even your humble phone charger has a VA rating, though it's usually quite small. It tells you how much apparent power the charger needs from the wall outlet. This is important if you're plugging multiple chargers into a single power strip; you need to make sure the total VA demand doesn't exceed the power strip's capacity.
And don't forget Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS). UPS systems are used to provide backup power during outages. Their VA rating indicates how much equipment they can support, which is crucial for protecting critical devices like computers and servers from data loss or damage.

Fichas Para Sílabas Va Ve Vi Vo Vu Materiales Educativos Maestras
Power Factor
4. Making the Most of Your Electricity
We touched on power factor earlier, but it's worth diving deeper. Power factor is the ratio of real power (Watts) to apparent power (VA). It's a number between 0 and 1, and it represents how efficiently electrical power is being used. A power factor of 1 means that all the apparent power is being used to do real work, which is ideal.
A low power factor, on the other hand, means that a significant portion of the apparent power is reactive power, which isn't contributing to useful work. This can lead to higher electricity bills, as you're paying for power that isn't actually doing anything. It can also cause problems for the utility company, as they have to generate and transmit more power than is actually being used.
So, what can you do about a low power factor? That's where power factor correction comes in. Power factor correction involves adding capacitors to the circuit to compensate for the inductive load (like motors) that cause reactive power. This improves the power factor, making the system more efficient and reducing electricity costs.
Think of it like this: a glass of beer with a lot of foam has a low "beer factor." Power factor correction is like adding more beer to the glass and reducing the foam, so you get more drink for your money. Simple, right?

Voltage vs. Volt-Amperes
5. Voltage and VA
To reiterate, let's make the distinctions between Voltage (V) and Volt-Amperes (VA) crystal clear. Voltage, as we mentioned earlier, is the electrical pressure that drives the current through a circuit. It's what makes the electrons move. Without voltage, there's no current, and no electricity.
Volt-Amperes, on the other hand, is a measure of the total apparent power in an AC circuit. It takes into account both the voltage and the current, but it doesn't tell you how much of that power is actually being used to do work. It's like the total amount of effort being put in, regardless of the actual outcome.
The key difference is that voltage is a measure of electrical potential, while Volt-Amperes is a measure of apparent power. Voltage is a fundamental property of electricity, while Volt-Amperes is a calculated value that depends on both voltage and current.
Consider a garden hose. Voltage is like the water pressure at the faucet. Volt-Amperes is like the total volume of water flowing through the hose, including any wasted water due to leaks or inefficiencies. Understanding both is crucial for managing your "electrical garden" effectively!

100 Va Disability Pay 2025 Calculator Charis Phaidra
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still have questions swirling around in your head? No problem! Here are some frequently asked questions to clear up any remaining confusion.
Q: Is VA the same as Watts?A: Nope! Watts measure real power (the power that does work), while VA measures apparent power (the total power in the circuit, including reactive power). They're related but not the same.
Q: Why is VA higher than Watts in some cases?A: Because of reactive power! In AC circuits, some energy is stored and released by components like capacitors and inductors. This reactive power contributes to the VA but doesn't do any real work.
Q: How do I calculate VA?A: It's simple: VA = Voltage (V) x Current (A). Just remember to use the RMS (root mean square) values for voltage and current in AC circuits.
Q: What is a good power factor?A: Ideally, you want a power factor as close to 1 as possible. A power factor of 0.9 or higher is generally considered good.