Beautiful Work Tips About What Is IPv4 And IPv6
IPv4 Vs IPv6 Understanding The Differences (2023)
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding the Internet's Language
Ever wonder how your computer talks to other computers across the vast expanse of the internet? Well, it's not through secret handshakes or telepathy (though that would be cool!). Instead, they use a set of rules, kind of like a universal language, to find each other and exchange information. This language is built upon something called IP addresses, and the two main versions you'll hear about are IPv4 and IPv6. Think of them as different dialects of the same internet language.
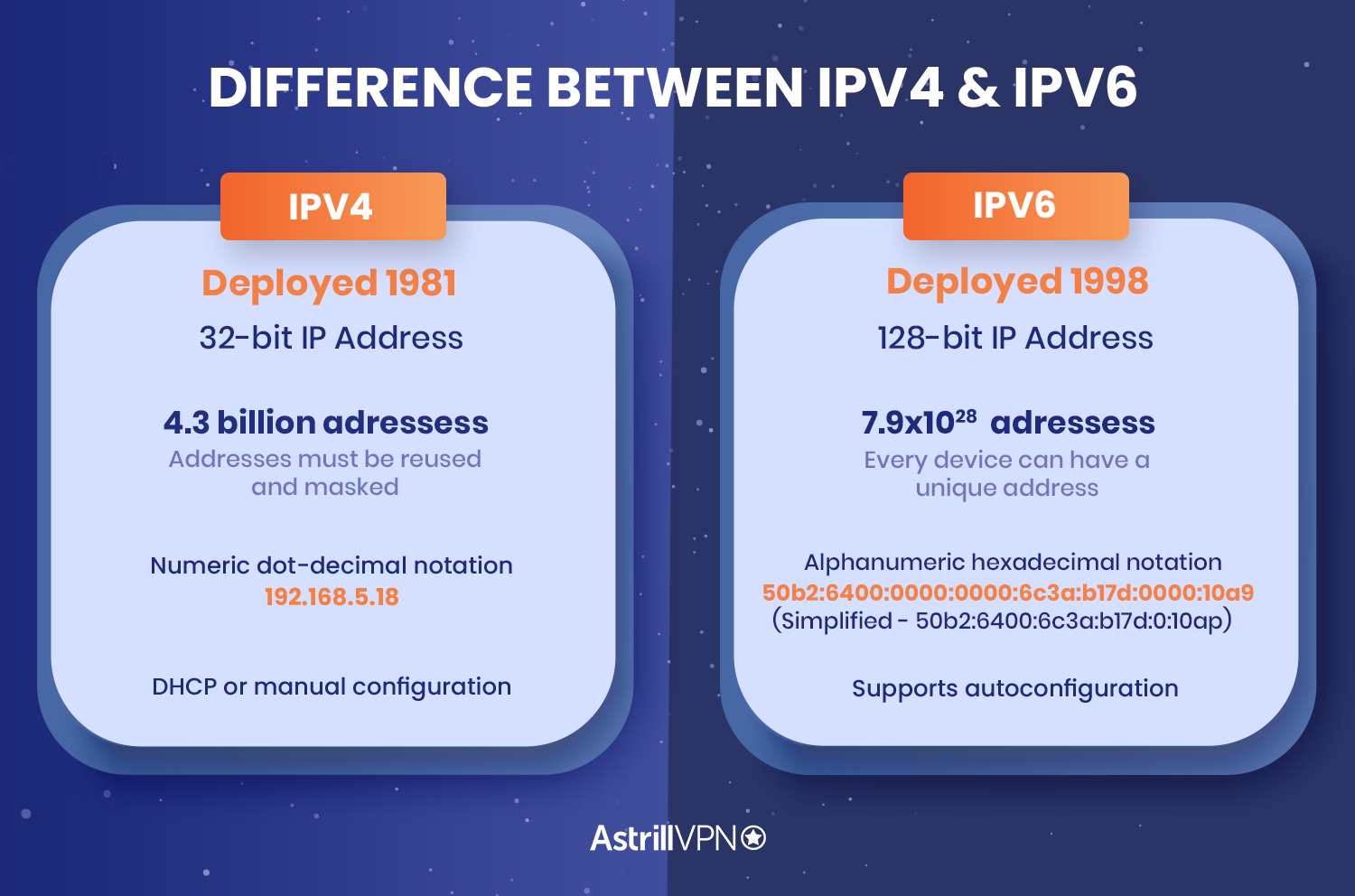
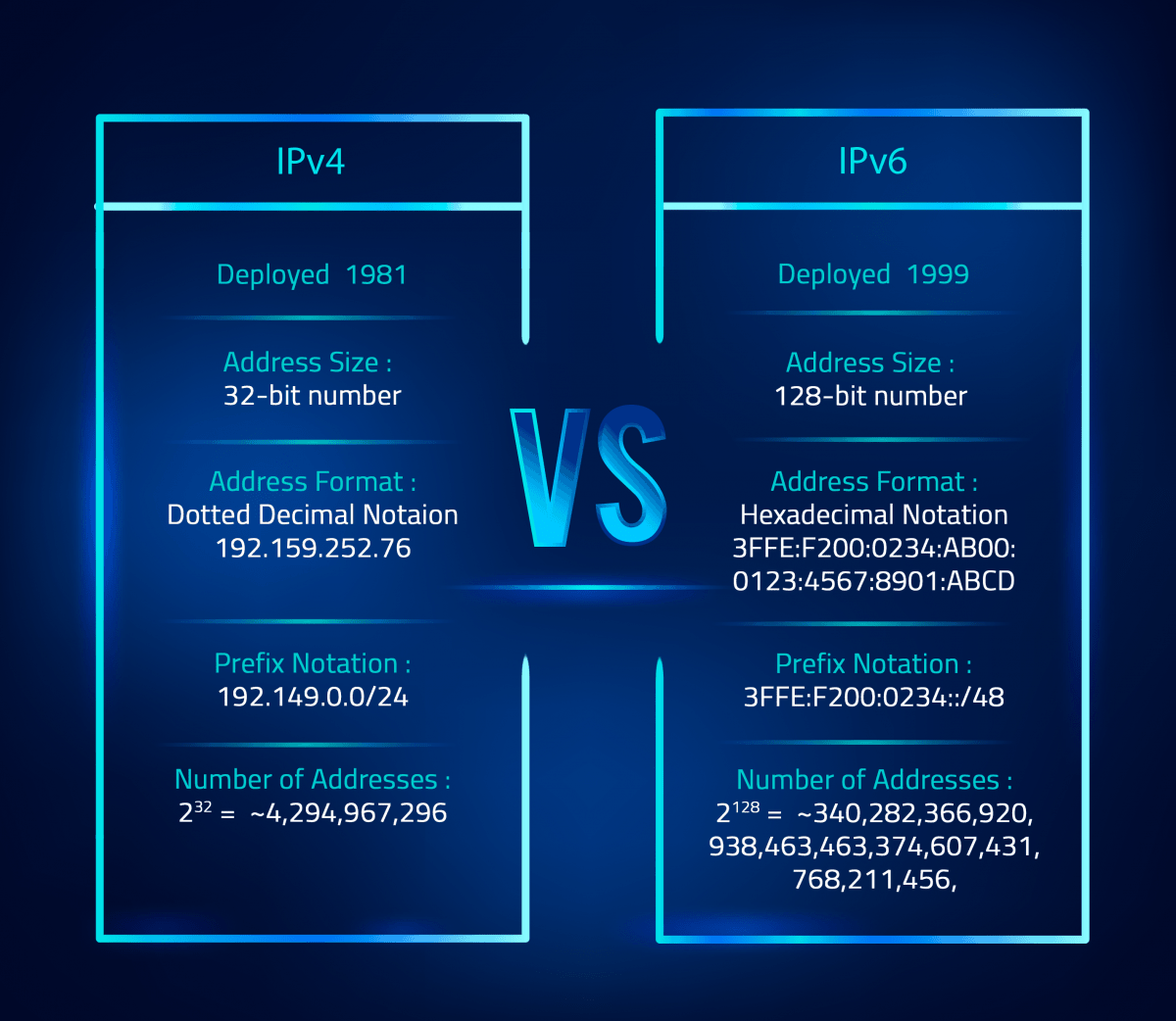
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) has been the workhorse of the internet for decades. It's like that trusty old car that's been reliable but is starting to show its age. It uses a 32-bit addressing system, which means it can create roughly 4.3 billion unique addresses. Sounds like a lot, right? But with billions of devices connecting to the internet these days — from smartphones and smartwatches to refrigerators and, well, everything — we're starting to run out of IPv4 addresses. Imagine trying to find your friend in a city where everyone has the same street number!
Thats where IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) comes into the picture. Its the shiny, new, super-efficient addressing system thats designed to solve the IPv4 address exhaustion problem. With a whopping 128-bit addressing system, IPv6 can theoretically create 340 undecillion addresses. That's a number so big its almost impossible to wrap your head around — more than the number of grains of sand on Earth! In other words, we won't be running out of IPv6 addresses anytime soon.
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is like moving from a small town with a simple address system to a massive metropolis with a sophisticated, multi-layered addressing system. Its necessary to accommodate the growing internet population, but it also requires changes to networks and devices to ensure compatibility. It's a bit like learning a new language; there might be a slight learning curve, but in the end, it allows for better communication and expansion. IPv4 is a noun. IPv6 is a noun.
/IPv4-vs-IPv6-EN.png?width=1320&name=IPv4-vs-IPv6-EN.png)
IPv4 Vs. IPv6 What It Means & Key Differences Explained
The Key Differences
2. Breaking Down the Technicalities (Without Getting Too Technical)
Okay, let's dive a little deeper into what makes IPv4 and IPv6 different, but we'll keep it nice and simple. The most obvious difference, as we mentioned, is the address format. IPv4 addresses are typically written in decimal notation, like 192.168.1.1, while IPv6 addresses use hexadecimal notation, like 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. Don't worry, you don't need to memorize those!
Aside from the address format, IPv6 offers several other advantages over IPv4. One major benefit is improved security. IPv6 supports built-in security features like IPSec (Internet Protocol Security), which provides encryption and authentication for network traffic. This helps to protect data from being intercepted or tampered with while its traveling across the internet. It's like sending a letter in a locked box instead of just tossing it in the regular mailbox.
Another key difference is how IPv6 handles network configuration. IPv4 often relies on DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to assign IP addresses to devices automatically. IPv6, on the other hand, supports stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC), which allows devices to configure themselves without the need for a DHCP server. This simplifies network management and makes it easier to deploy IPv6 on large networks.
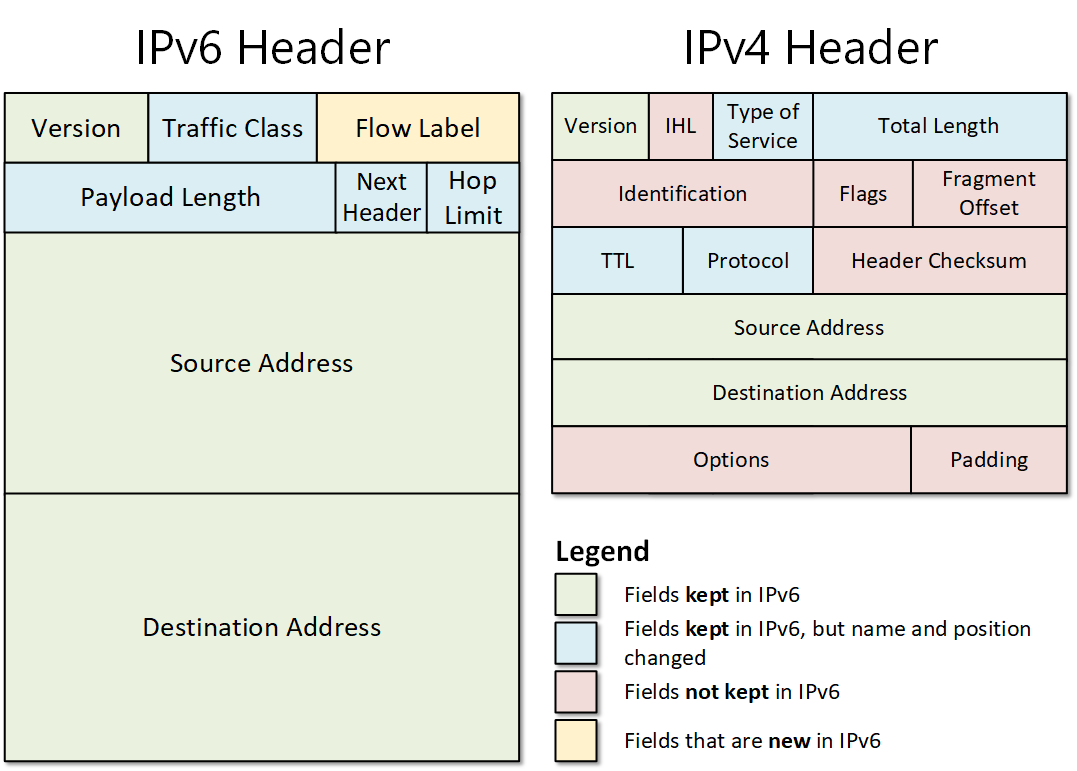
Furthermore, IPv6 is designed to be more efficient than IPv4 in terms of routing and packet processing. It uses a simpler header format, which reduces the overhead associated with processing packets. This can lead to faster network performance and lower latency, especially for applications that require real-time communication, like online gaming or video conferencing. Think of it as streamlining the postal service to get packages delivered faster.
Ipv4 E Ipv6 Que Son Para Sirven Y Como Se Usan En Vrogue.co
Why the Shift to IPv6 Matters
3. The Future of the Internet is IPv6
So, why is everyone talking about IPv6? Well, besides the looming IPv4 address exhaustion, IPv6 offers some tangible benefits that make it worth the effort of upgrading. As more and more devices connect to the internet, the need for IPv6 becomes increasingly critical. From smart homes to autonomous vehicles, the internet of things (IoT) is driving the demand for more IP addresses and improved network performance.
IPv6 also plays a key role in enabling new technologies and applications. For example, IPv6 supports mobility features that allow devices to seamlessly switch between different networks without losing their IP address. This is particularly important for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets that are constantly moving between Wi-Fi and cellular networks. Imagine being able to walk around a city without having to reconnect to a new Wi-Fi network every block.
Another reason why the shift to IPv6 matters is that it can improve the overall user experience. With faster network speeds, lower latency, and enhanced security, IPv6 can make browsing the web, streaming videos, and playing online games a more enjoyable experience. It's like upgrading from dial-up to broadband — once you experience the speed and responsiveness of a faster connection, you'll never want to go back.
While the transition to IPv6 may seem daunting, its a necessary step to ensure the continued growth and innovation of the internet. As more and more websites and services adopt IPv6, it will become increasingly important for individuals and organizations to support it as well. The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is an ongoing process that will continue to shape the future of the internet for years to come.

How IPv4 and IPv6 Impact You
4. Understanding the User Perspective
You might be thinking, "Okay, this all sounds interesting, but how does it actually affect me?" Well, depending on your internet service provider (ISP) and the websites you visit, you may already be using IPv6 without even realizing it. Many ISPs have already deployed IPv6 on their networks, and more and more websites are becoming IPv6-enabled. In fact, major content providers like Google and Facebook have been strong advocates for IPv6 adoption.
If you're using an older router or operating system, you may need to upgrade to ensure that you can take advantage of IPv6. Most modern devices support IPv6 out of the box, but it's always a good idea to check your settings to make sure that it's enabled. You can also use online tools to test whether your device is using IPv6. Just search for "IPv6 test" in your favorite search engine.
For most users, the transition to IPv6 will be seamless and transparent. You won't need to change your browsing habits or learn any new skills. In fact, you may not even notice that you're using IPv6. However, the benefits of IPv6, such as faster speeds and improved security, will ultimately enhance your online experience. It's like getting a free upgrade to a better internet experience.
While the technical details of IPv4 and IPv6 might seem complex, the underlying goal is simple: to make the internet a better place for everyone. By supporting IPv6, you're helping to ensure that the internet can continue to grow and evolve to meet the needs of future generations. It's a small step that can make a big difference in the long run.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
5. Your Burning Questions Answered
Let's address some of the common questions people have about IPv4 and IPv6.
6. Question 1
Answer: Don't worry! Even if a website only supports IPv4, your device can still access it. Your ISP will use a technology called Network Address Translation (NAT) to translate your IPv6 address into an IPv4 address, allowing you to connect to the website. It's like having a translator who can speak both languages.
7. Question 2
Answer: No, you don't need to disable IPv4. In fact, it's best to leave both IPv4 and IPv6 enabled on your device. This allows you to connect to both IPv4 and IPv6 websites seamlessly. Most devices are configured to prefer IPv6 over IPv4, so if both protocols are available, your device will automatically use IPv6.
8. Question 3
Answer: Yes, IPv6 is generally considered to be more secure than IPv4. IPv6 supports built-in security features like IPSec, which provides encryption and authentication for network traffic. This helps to protect data from being intercepted or tampered with. However, it's important to note that security is an ongoing process, and even with IPv6, it's still important to use strong passwords, keep your software up to date, and be cautious about clicking on suspicious links.