Ideal Info About What Happens In Phase 0
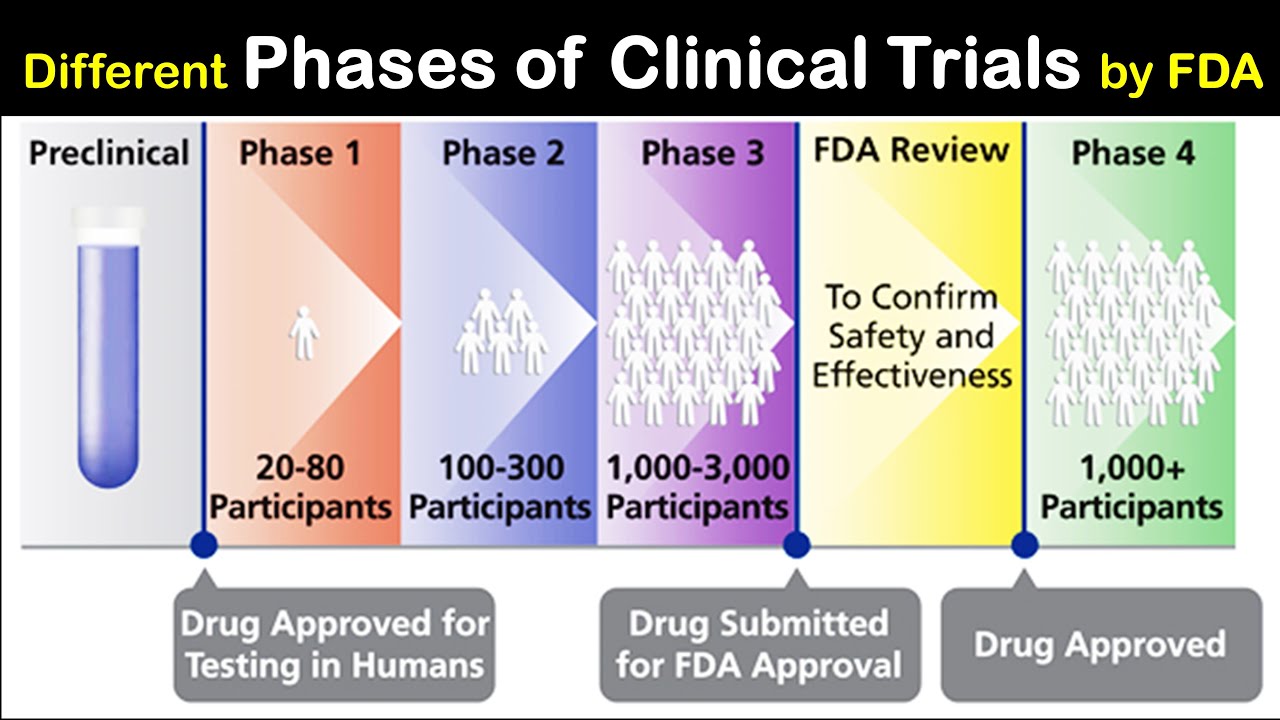
Decoding Phase 0
1. Laying the Foundation for a Scalable Future
Alright, let's talk about Phase 0 of Ethereum 2.0. Think of it as the very first brick laid in building a magnificent digital cathedral. It's where the magic begins, setting the stage for a more scalable, secure, and sustainable Ethereum. It wasn't just a flip of a switch; it was a carefully orchestrated launch of a whole new system running parallel to the existing Ethereum 1.0.
Phase 0 essentially introduced the Beacon Chain. This is the central coordination hub for the new Ethereum 2.0 system. It's not directly processing transactions like the main Ethereum chain we're used to. Instead, it's managing the validators and overseeing the transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). Think of it as the conductor of an orchestra, ensuring all the instruments (validators) play in harmony.
Without Phase 0, theres no Ethereum 2.0 as we know it. Its the bedrock. It established the rules, the infrastructure, and the consensus mechanism that future phases would build upon. Before Phase 0, the idea of a fully PoS Ethereum was just that: an idea. This phase made it a tangible reality, putting the pieces in place for a more energy-efficient and scalable network.
So, what's the big deal with Proof-of-Stake? Well, imagine instead of computers racing to solve puzzles (Proof-of-Work), validators "stake" their ETH to have a chance to propose and validate new blocks. This uses significantly less energy and opens up opportunities for more people to participate in securing the network. It's like switching from a gas-guzzling monster truck to a fleet of sleek, efficient electric cars.

Phase 0 Fastest Contract Research Organization TRACER
What Exactly Happens in Phase 0?
2. Diving Deeper into the Beacon Chain
Okay, so we know Phase 0 is important, but what actually happens? The main event is the launch of the Beacon Chain. This chain is responsible for managing the validator set, the heart of the Ethereum 2.0 Proof-of-Stake system. These validators are the ones who propose and attest to new blocks, ensuring the network's integrity.
One crucial aspect of Phase 0 was enabling ETH holders to stake their ETH to become validators. To become a validator, one needed to deposit 32 ETH into a special smart contract on the Ethereum 1.0 chain. This deposit effectively locks up the ETH and registers the validator on the Beacon Chain. Its a bit like buying a share in the network, giving you both responsibility and potential rewards.
The Beacon Chain uses the Casper FFG (Friendly Finality Gadget) consensus mechanism. This is a hybrid approach that combines Proof-of-Stake with Byzantine Fault Tolerance. Essentially, it ensures that even if a certain number of validators act maliciously, the network can still reach consensus and remain secure. This adds a layer of robustness to the system, making it resistant to attacks.
The Beacon Chain also generates randomness, which is used to select validators to propose new blocks and attest to existing ones. This randomness helps to prevent collusion and ensure a fair distribution of rewards. Its a bit like a lottery, but instead of winning money, you're winning the chance to validate transactions and earn ETH.
The Significance of Validators in Phase 0
3. Guardians of the Network
Validators are the unsung heroes of Phase 0, and indeed, of Ethereum 2.0 in general. They are the backbone of the new Proof-of-Stake system, responsible for securing the network and ensuring its smooth operation. Their role is crucial in maintaining the integrity and reliability of the chain.
To become a validator, an individual or entity needs to stake 32 ETH. This acts as a financial commitment to the network. If a validator acts maliciously or fails to fulfill their duties, they risk losing their staked ETH, which is known as "slashing." This incentivizes validators to act honestly and responsibly.
Validators perform several key functions. They propose new blocks to the Beacon Chain, attest to the validity of existing blocks, and participate in consensus mechanisms. By performing these functions, they earn rewards in the form of newly minted ETH. It's a win-win situation: they secure the network and earn income in the process.
The Beacon Chain actively manages the validator set, ensuring that there are enough validators online to maintain network security. It also manages the distribution of rewards and penalties, incentivizing good behavior and discouraging malicious actions. The whole system is designed to create a stable and reliable validator ecosystem.

3 Cardiac Action Potential The Various Phases (phase 0 To Phase 4) Of
How Phase 0 Paved the Way for Future Upgrades
4. Building Blocks for a Brighter Future
Phase 0 wasn't just an end in itself; it was the crucial foundation upon which all future Ethereum 2.0 upgrades would be built. It established the core infrastructure and consensus mechanisms that would be expanded upon in subsequent phases. Without Phase 0, there would be no roadmap to a more scalable and efficient Ethereum.
One of the most significant ways Phase 0 paved the way for future upgrades was by introducing the Beacon Chain. This chain serves as the central coordination hub for the entire Ethereum 2.0 system, managing validators, generating randomness, and overseeing the transition to Proof-of-Stake. Its the command center for the Ethereum 2.0 spaceship.
Phase 0 also provided valuable insights and learnings that informed the design and implementation of subsequent phases. By observing the performance of the Beacon Chain and the behavior of validators, developers were able to identify areas for improvement and refine their approach. It was a real-world testbed for the new Ethereum 2.0 system.
Looking ahead, Phase 0's impact will continue to be felt as Ethereum 2.0 evolves and matures. The core principles and technologies established in Phase 0 will remain fundamental to the network's operation, ensuring its continued security, scalability, and sustainability. It was the spark that ignited the Ethereum 2.0 revolution.
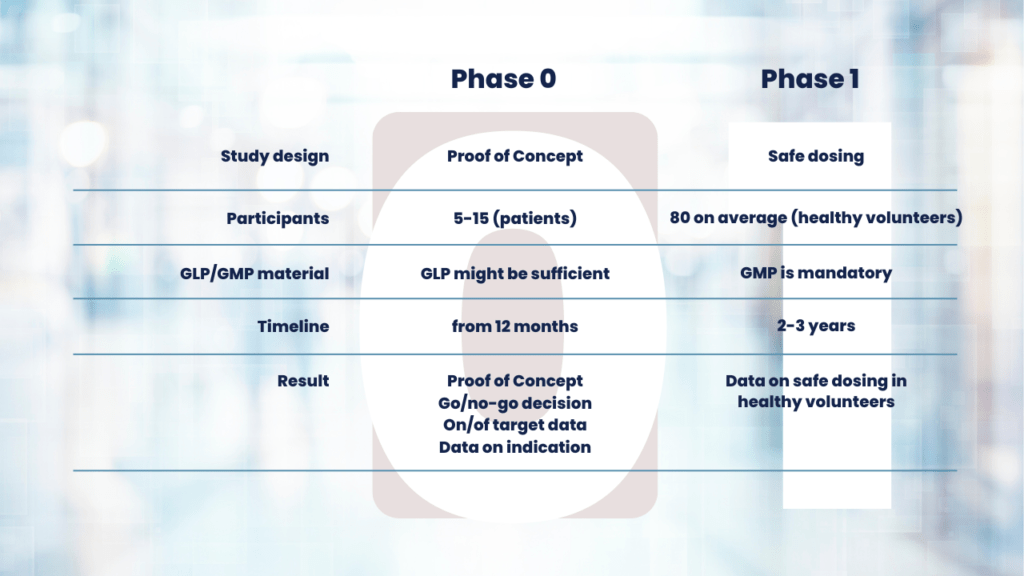
Phase 0 Fastest Contract Research Organization TRACER
Whats Next After Phase 0?
5. The Road Ahead for Ethereum 2.0
So, Phase 0 is in the rearview mirror, but what does the future hold? The Ethereum roadmap is a long and winding road, but the destination is a vastly improved Ethereum network. Think of it as upgrading from a bicycle to a high-speed train. The next steps involve incorporating sharding and further optimizing the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism.
Sharding is a technique that divides the Ethereum blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces called "shards." This allows the network to process transactions in parallel, significantly increasing its throughput. Imagine a highway expanding from one lane to multiple lanes — more traffic can flow smoothly.
As Ethereum 2.0 continues to develop, we can expect to see even greater scalability, security, and sustainability. The network will be able to handle a much larger volume of transactions, making it more suitable for a wider range of applications. And with the reduced energy consumption of Proof-of-Stake, Ethereum will become a much greener and more environmentally friendly blockchain.
The future of Ethereum is bright, and Phase 0 was the crucial first step on this exciting journey. By laying the foundation for a more scalable and sustainable network, it set the stage for a new era of blockchain innovation. Buckle up, because the ride is just beginning!

A Model Of The Phase 0 Process, With Exemplary Subphases To Progress
Frequently Asked Questions About Phase 0
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Lets address some common questions about Phase 0 to clear up any lingering doubts.
Q: Why was Phase 0 necessary?
A: Phase 0 was the crucial first step in transitioning Ethereum to a Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism and laying the groundwork for a more scalable and sustainable network. It introduced the Beacon Chain, which manages validators and coordinates the new system.
Q: Can I still become a validator after Phase 0?
A: Absolutely! The opportunity to become a validator is ongoing. You'll need 32 ETH to stake and meet the technical requirements, but its a continuous process.
Q: What's the difference between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0?
A: Ethereum 1.0 is the original Ethereum blockchain that uses Proof-of-Work. Ethereum 2.0 is the upgraded version that uses Proof-of-Stake and sharding to achieve greater scalability and efficiency. Think of it like upgrading your old computer to a brand new, super-powered machine.