Awesome Info About What Is The Difference Between Line Current And Phase

Understanding Line Current vs. Phase Current
1. The Core Concept
Okay, let's tackle something that might sound intimidating: the difference between line current and phase current. Trust me, its not about to send you into a circuit overload. Think of it like this: you're looking at the same river (electricity), but from different bridges (points in the electrical system). Line current is the view from a major highway bridge, seeing all the flow at once. Phase current is peering from a smaller, more local bridge, just checking the flow in a specific channel.
In essence, we're talking about alternating current (AC) circuits, specifically polyphase systems like the three-phase power thats commonly used to power factories and large buildings. These systems deliver power more efficiently than single-phase, but they also bring some interesting complexities to how we measure current.
Consider a balanced three-phase system. Imagine three identical power sources, each delivering its electrical goodness, but offset in time. That offset is key. Because of it, the current in each individual phase isn't necessarily the same as the total current flowing in the wires that connect the load back to the source.
So, to make things clear, lets break down each type of current individually. Well then dive into how they relate, particularly in different configurations, and why understanding the difference even matters. Don't worry, we'll avoid complicated equations for now — mostly! We're focusing on the concepts, not the calculations, although a little math might peek its head in later on!

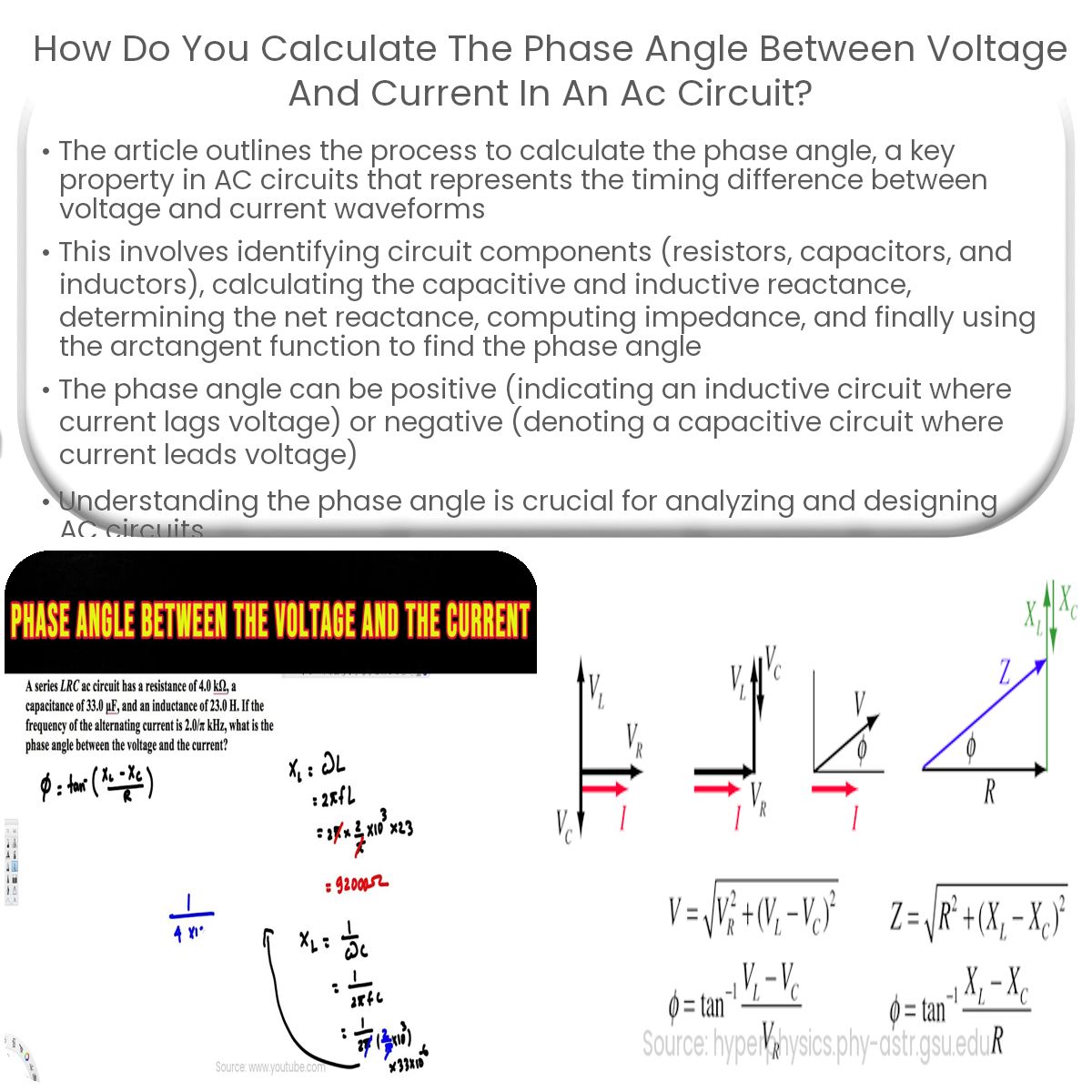
Explained Line Voltage, Current, Phase Current
Phase Current
2. Focusing on Each Leg of the Journey
Phase current is the current flowing through a single winding or "leg" of a polyphase system. Think of it like the amount of water flowing through a single pipe in a multi-pipe system. In a three-phase motor, for instance, each of the three windings has its own phase current. This is the current that determines how much each individual component is "working."
In a balanced three-phase system (where all the phases are equally loaded — sharing the work), the phase currents should ideally be equal in magnitude. However, in the real world, things rarely go exactly as planned. Uneven loads can cause imbalances, leading to different phase currents. This is something engineers watch out for, as significant imbalances can lead to inefficiency and even damage.
The magnitude of phase current is directly related to the power delivered by that specific phase and the voltage across it. It's a crucial parameter for understanding the load distribution and performance of individual components within a polyphase system.
Imagine baking a three-layer cake. Each layer contributes to the overall deliciousness (total power). The phase current would be like measuring the ingredients used only for one specific layer. You need that measurement to make sure that the layers are balanced and the cake doesnt collapse!

What Is Difference Between Line And Load
Line Current
3. Seeing the Total Flow
Line current, on the other hand, is the current flowing through the conductors that connect the power source to the load. These are the actual wires you see running to the equipment. This is the total current traveling from the source to the load.
The relationship between line current and phase current depends on how the windings of the power source or load are connected. The two most common configurations are "star" (also known as wye) and "delta." In a star connection, the line current and phase current are the same thing — easy peasy! But in a delta connection, things get a little more interesting.
In a delta connection, the line current is actually greater than the phase current. Specifically, the line current is equal to the square root of 3 (approximately 1.732) times the phase current. This is because the line current has to split and feed into two different phases.
Think of line current as the total traffic on a major highway leading to a city. It's the combined flow of all the vehicles heading towards different destinations within the city. Understanding line current is crucial for sizing wires and protective devices (like circuit breakers) to ensure the system can handle the total current demand safely.

Star (Wye) vs. Delta
4. Decoding the Electrical Wiring Diagram
The relationship between line and phase currents dramatically changes depending on whether we're dealing with a star (Y or Wye) or delta (Δ) connection. These are two fundamental ways of wiring three-phase systems, and they behave very differently. So, let's break them down.
In a star (Wye) connection, the ends of each phase winding are connected to a common neutral point. This neutral point can be grounded, providing a reference for voltage measurements. The crucial detail here is that the line current is equal to the phase current. What flows in the line conductor also flows through the phase winding. Easy to remember!
However, with voltage, things are different in a star connection. The line voltage (voltage between two line conductors) is equal to the square root of 3 times the phase voltage (voltage across one phase winding). It's like the voltage gets "multiplied" across the lines.
Now, for the delta connection, things get a little trickier. Here, the phase windings are connected end-to-end, forming a closed loop (the delta shape). There's no neutral point in a simple delta connection. What makes this different? The line current is equal to the square root of 3 times the phase current. So, the current gets "multiplied" in the lines!
But the voltage is simpler in a delta connection. The line voltage is equal to the phase voltage. What you measure across the line is the same as what's across a phase winding. Knowing whether you have a star or delta connection is absolutely critical for correctly calculating currents and voltages and ensuring your electrical system is operating safely and efficiently.
Why Does It All Matter? Practical Applications
5. From Safety to Efficiency
Understanding the difference between line current and phase current isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has very real and practical applications. Getting it wrong can lead to some serious problems!
One of the most important applications is correctly sizing wires and protective devices. Wires need to be able to handle the current flowing through them without overheating and causing a fire. Circuit breakers and fuses need to be sized to trip and protect the system from overloads. If you're calculating the wrong current, you could end up with wires that are too small or protective devices that are too large, leaving your system vulnerable to damage or even fire.
Another critical area is motor control and protection. Motors are often connected in either star or delta configurations, and the currents flowing through the windings and the supply lines will vary accordingly. Incorrectly setting motor protection relays based on a misunderstanding of line and phase currents can lead to nuisance tripping (unnecessary shutdowns) or, even worse, damage to the motor.
Finally, understanding these concepts is vital for power system analysis and troubleshooting. When diagnosing problems in a three-phase system, knowing the expected relationship between line and phase currents can help pinpoint faults and identify imbalances. This can save time and money by allowing for faster and more accurate repairs.

Phase Current Calculator
FAQ
6. Clearing Up the Confusion
Still scratching your head? Don't worry, here are some frequently asked questions to help solidify your understanding:
Q: What happens if the phases are unbalanced?
A: In an unbalanced system, the phase currents will no longer be equal. This can cause increased neutral current, overheating, and reduced efficiency. It's important to identify and correct imbalances as quickly as possible.
Q: How do I measure line and phase currents?
A: You can use clamp-on ammeters to measure line currents directly on the conductors. Measuring phase currents often requires accessing the motor windings or using specialized equipment.
Q: Is it okay to simplify things and just use one current value?
A: While simplifying can be tempting, it's generally not a good idea. Using the wrong current value can lead to incorrect calculations and potentially dangerous situations. Always consider the specific context and connection type.