Beautiful Info About CAN Bus L And H
What Is CAN Bus & How To Use Interface With ESP32 And Arduino
Understanding CAN Bus L and H
1. What are CAN Bus L and H? (It's simpler than it sounds!)
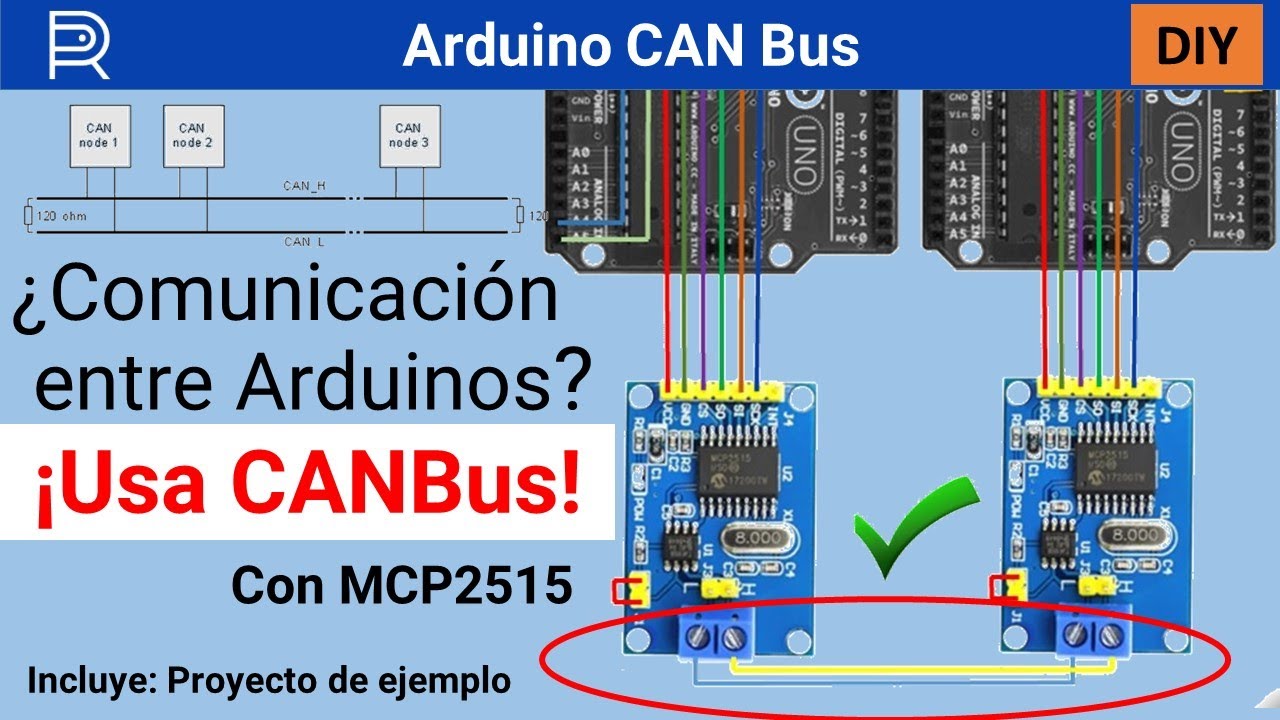
Ever wondered how all the different parts of your car "talk" to each other? It's not like they're shouting across the engine bay, right? The answer, in many modern vehicles, lies within something called a CAN bus. And a crucial part of that CAN bus are two wires: CAN bus L and CAN bus H. Think of them as the digital nervous system of your car. These two little wires are responsible for carrying messages between all the electronic control units (ECUs) within your vehicle, from the engine control module to the anti-lock braking system.
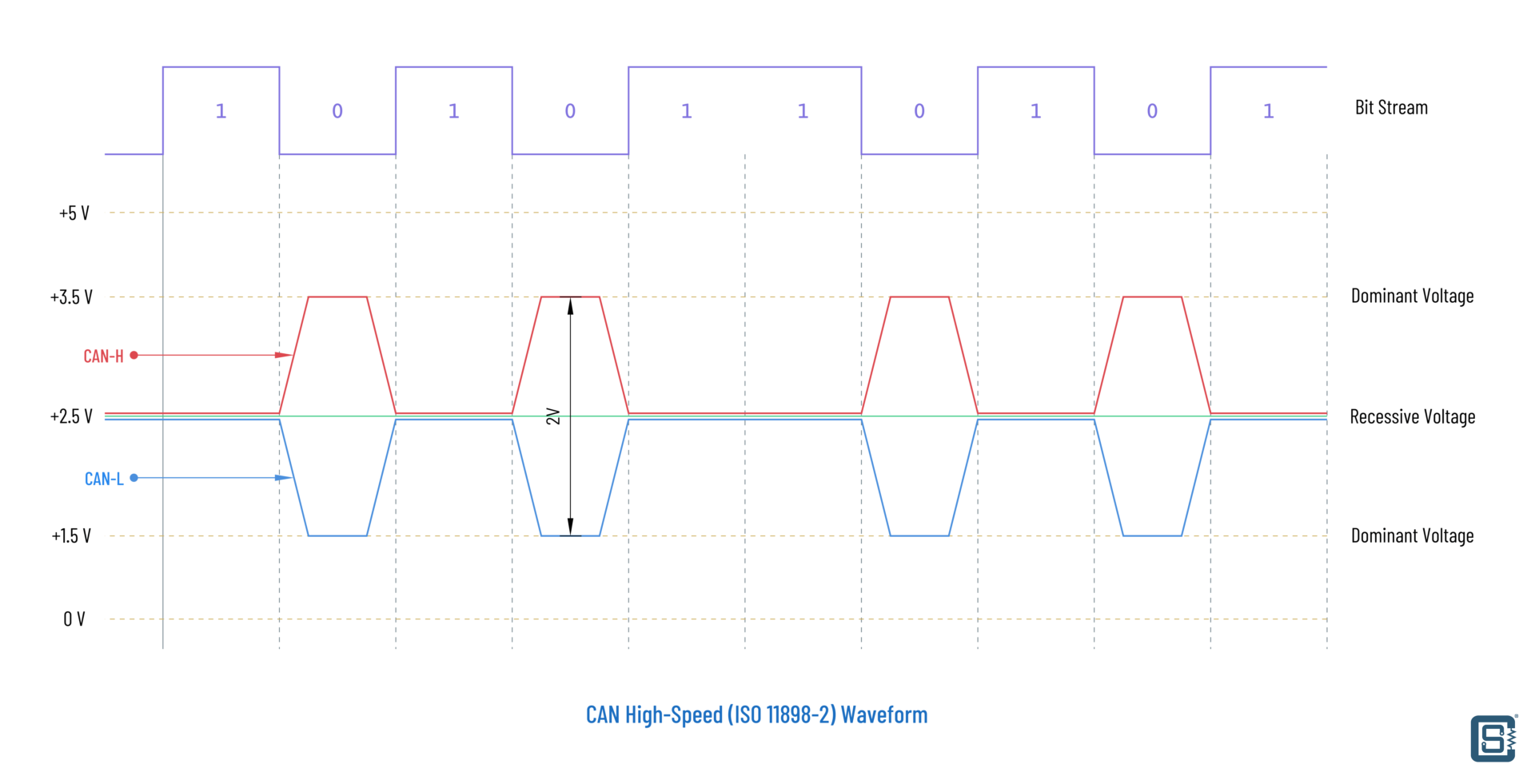
Now, the "L" and "H" stand for "Low" and "High," respectively. They represent the two different voltage levels used to transmit data across the CAN bus. Instead of just one wire sending a signal, the CAN bus uses a differential signaling scheme, which is a fancy way of saying that it uses the difference in voltage between the L and H wires to represent the data. This helps to make the communication more reliable and less susceptible to noise and interference — crucial in the electrically noisy environment of a car.
Imagine it like this: instead of just yelling your message (which is easily misunderstood in a noisy room), you have two people whispering different things, and the difference between what they're whispering is the actual message. It's much clearer and more reliable, right? That's the basic idea behind CAN bus L and H.
So, CAN bus L and H aren't just random wires; they're the vital arteries through which digital information flows, enabling your car's systems to cooperate and function as a cohesive unit. Without them, your modern vehicle would be about as useful as a brick.

Delving Deeper
2. The Magic of Differential Signaling Explained
Okay, let's get a little more technical (but still keep it approachable!). The magic behind CAN bus L and H lies in something called differential signaling. In a nutshell, instead of sending a signal on a single wire, the CAN bus sends two signals simultaneously, one on the CAN bus H wire and one on the CAN bus L wire. The data is encoded as the difference between these two signals.
Why do this? Well, for several reasons. First and foremost, it significantly improves noise immunity. Any noise or interference that affects both wires equally (a common occurrence in a car's electrical system) will be cancelled out because it doesn't change the difference between the signals. Think of it like having a conversation in a crowded room. If everyone is yelling the same thing, you still can't understand anything. But if two people whisper different parts of the message, you can filter out the noise and understand the actual message.
Secondly, differential signaling reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI). Because the signals on the CAN bus L and H wires are generally equal and opposite, the electromagnetic fields they generate tend to cancel each other out. This helps to prevent the CAN bus from interfering with other electronic systems in the vehicle.
Finally, the use of differential signalling allows for reliable data transmission over longer distances. This is especially important in larger vehicles, such as trucks and buses, where the distance between ECUs can be significant. So, CAN bus L and H aren't just two random wires; they're part of a carefully engineered system designed for robust and reliable communication.

CAN Bus Serial Communication How It Works? YouTube
Troubleshooting CAN Bus L and H Issues
3. When Things Go Wrong
So, what happens when things go wrong with your CAN bus? Unfortunately, CAN bus problems can manifest in a variety of ways, making diagnosis a bit of a challenge. Some common symptoms include warning lights on your dashboard (like the check engine light, ABS light, or traction control light), intermittent or complete failure of certain vehicle systems (like power windows, door locks, or even the engine), and error codes stored in the vehicle's computer.
If you suspect a CAN bus issue, the first step is to scan the vehicle's computer for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). A scan tool (which you can buy or borrow from a friend or local auto parts store) can read these codes and provide valuable clues about the nature of the problem. Specific codes related to CAN bus communication failures, such as "CAN bus off" or "CAN bus communication error," are strong indicators of a CAN bus problem.
Once you have the DTCs, you can start troubleshooting. Common causes of CAN bus problems include wiring issues (like shorts, opens, or corrosion), faulty ECUs, and termination resistor problems. A multimeter can be used to check the continuity and voltage levels of the CAN bus L and H wires. Pay close attention to the termination resistors at the ends of the CAN bus, as these are critical for proper communication. These resistors are usually 120 ohms. An open or shorted resistor will cause problems.
Remember, working with vehicle electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. If you're not comfortable working with electricity, it's always best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic. However, with a little knowledge and the right tools, you can often diagnose and fix common CAN bus problems yourself. Replacing an ECU, if diagnosed to be the root cause can be costly, so thorough diagnosis is key. Often times aftermarket electronics improperly installed can cause CAN bus issues.
The Future of CAN Bus
4. Looking Ahead
While CAN bus has been the dominant communication protocol in vehicles for decades, it's not without its limitations. As vehicles become increasingly complex and connected, the demands on the communication network are growing. This has led to the development of new and improved communication technologies, such as CAN FD (CAN with Flexible Data-rate) and Automotive Ethernet.
CAN FD offers significantly higher data rates than traditional CAN bus, allowing for faster communication between ECUs. This is particularly important for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving applications, which require the exchange of large amounts of data in real-time. As more and more features are packed into modern vehicles, CAN FD provides the extra bandwidth to allow it to all work smoothly.
Automotive Ethernet, on the other hand, provides even higher data rates and supports more advanced networking protocols. It's often used for in-vehicle infotainment systems, camera systems, and other high-bandwidth applications. Think of it as the broadband internet connection for your car. The higher throughput allows for improved vehicle communication and performance.
While CAN bus is likely to remain a part of vehicle communication systems for the foreseeable future, these newer technologies are poised to play an increasingly important role in the years to come. The future of vehicle communication is all about faster, more reliable, and more secure data transfer. It should be noted that CAN is still used extensively and will be for a very long time. The industry is simply evolving with the introduction of new technologies.

Le Bus CAN Comment A Marche
CAN Bus L and H
5. Why Understanding This Tech Matters
So, there you have it. CAN bus L and H might seem like just a couple of wires, but they're actually a vital part of how your modern car functions. They're the silent communicators, the digital messengers that allow all the different systems in your vehicle to work together seamlessly. Whether you're a car enthusiast, a technician, or just a curious driver, understanding the basics of CAN bus technology can give you a deeper appreciation for the complexity and ingenuity of modern vehicles.
Knowing about CAN bus L and H can also be incredibly helpful when troubleshooting problems. Instead of just blindly replacing parts, you can use your knowledge of CAN bus to narrow down the potential causes of a problem and save yourself time and money. With the right tools and a little bit of patience, you can even fix some common CAN bus problems yourself. Think of the savings!
And as vehicles continue to evolve, understanding CAN bus and its successors will become even more important. As cars become more connected, autonomous, and data-driven, the communication network will play an increasingly critical role. So, take the time to learn about CAN bus L and H. It's an investment in your understanding of the vehicles of today — and tomorrow.
It can be a bit daunting to dig into technical aspects of your car, but remember the basic principle that they all communicate with each other in a digital way and that the CAN bus system is what makes it all happen. This intricate system allows all the various components to work together seamlessly to deliver your driving experience. Keep learning about all these systems, and it will all start to make sense.
Can Bus Signal Oscilloscope At Jerry Benjamin Blog
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About CAN Bus L and H
6. Your Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about CAN bus L and H to further clarify this important aspect of automotive technology.
Q: What happens if one of the CAN bus wires is cut?
A: If one of the CAN bus wires (either L or H) is cut, the CAN bus communication will likely be disrupted. Depending on the specific vehicle and the location of the break, this could result in a variety of symptoms, ranging from warning lights on the dashboard to complete failure of certain vehicle systems. A complete loss of communication with one or more ECUs is also possible. It is critical that both wires are intact for the system to function.
Q: How can I test the CAN bus L and H wires?
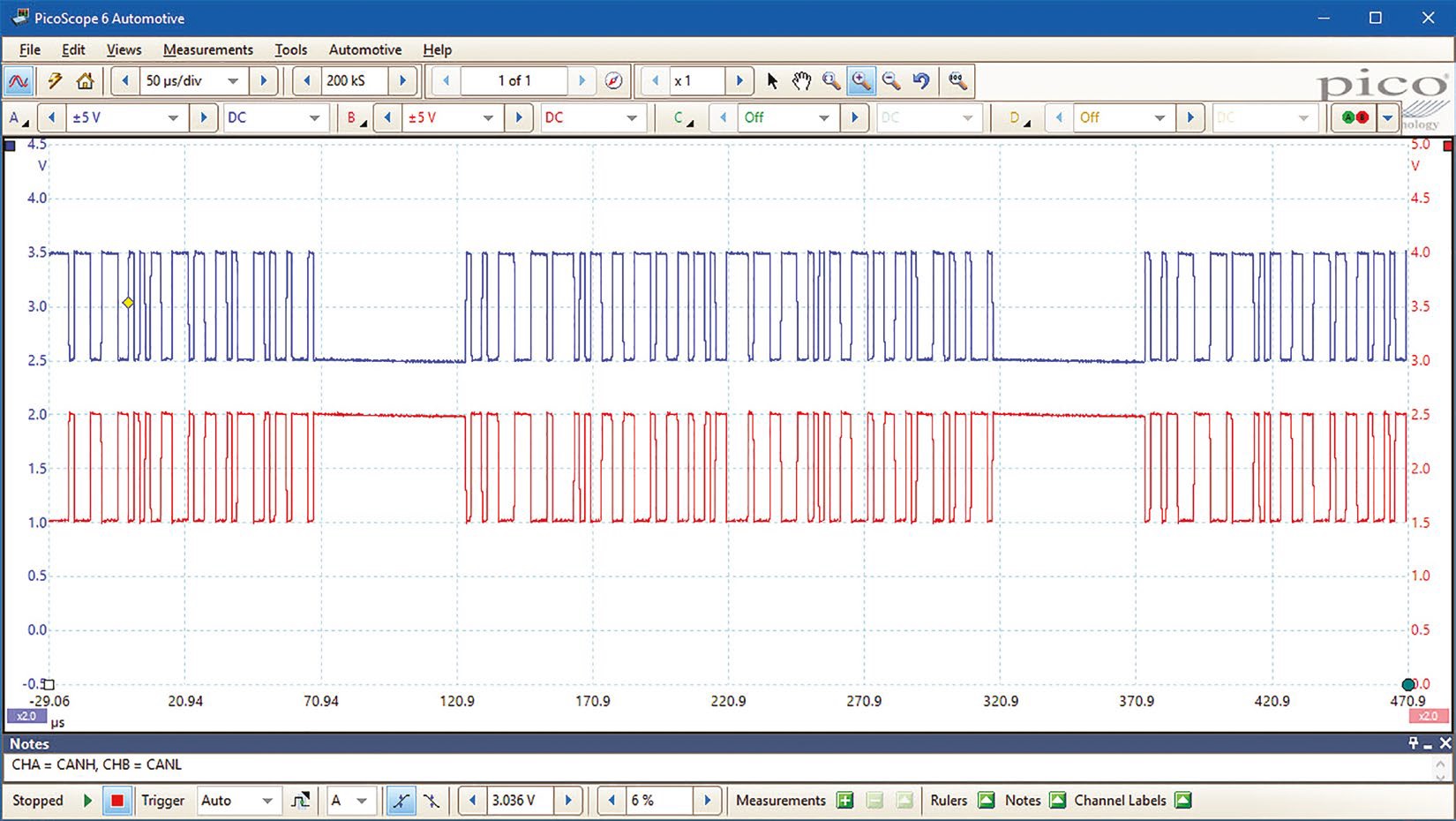
A: You can test the CAN bus L and H wires using a multimeter. First, check for continuity between the wires and ground to rule out any shorts. Then, measure the voltage levels on each wire. The specific voltage levels will vary depending on the vehicle and the CAN bus standard, but typically, the CAN bus H wire will be at a higher voltage than the CAN bus L wire. You can also use an oscilloscope to view the CAN bus signals and check for proper signal integrity.
Q: Are CAN bus L and H wires interchangeable?
A: No, the CAN bus L and H wires are not interchangeable. They carry different voltage levels and are designed to work together as a differential pair. Swapping the wires would disrupt the communication and likely cause errors. It is important to identify and connect the wires correctly to ensure proper CAN bus operation. The wiring harness should be labelled, but make sure to verify before connecting or reconnecting any wires.