What Everybody Ought To Know About At What Temperature Does LFP Battery Degrade
Are Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries Safe? A Comprehensive Guide
LFP Batteries
1. Understanding LFP Battery Degradation
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are gaining serious traction, and for good reason. They're safer and often more durable than some other lithium-ion chemistries. But even the toughest batteries have their limits. The keyword term we are focusing on is "At what temperature does LFP battery degrade," and it's a pretty important question to ask if you're relying on these powerhouses. "Degrade" here functions as a verb, describing the action of diminishing performance or lifespan.
Temperature is a major player in battery health. Think of it like this: batteries are like us. We don't perform our best when we're sweltering in extreme heat or shivering in the bone-chilling cold. LFP batteries are similar. While they boast impressive thermal stability compared to other lithium-ion cousins, pushing them outside their ideal temperature range can accelerate degradation.
But what exactly is that range? And how does temperature cause the degradation? Let's dig a little deeper, because knowing is half the battle. We want to keep those batteries running strong for as long as possible, right? Nobody wants to be replacing expensive battery packs prematurely.
Ultimately, understanding the temperature sensitivities of LFP batteries is key to maximizing their lifespan and ensuring reliable performance. It's about more than just avoiding extremes; it's about understanding the subtle ways temperature impacts the internal chemistry and physical structure of the battery over time.

The Influence Of Lithium Precipitation And SEI Film On Battery
The Sweet Spot
2. Finding the Goldilocks Zone for LFP Performance
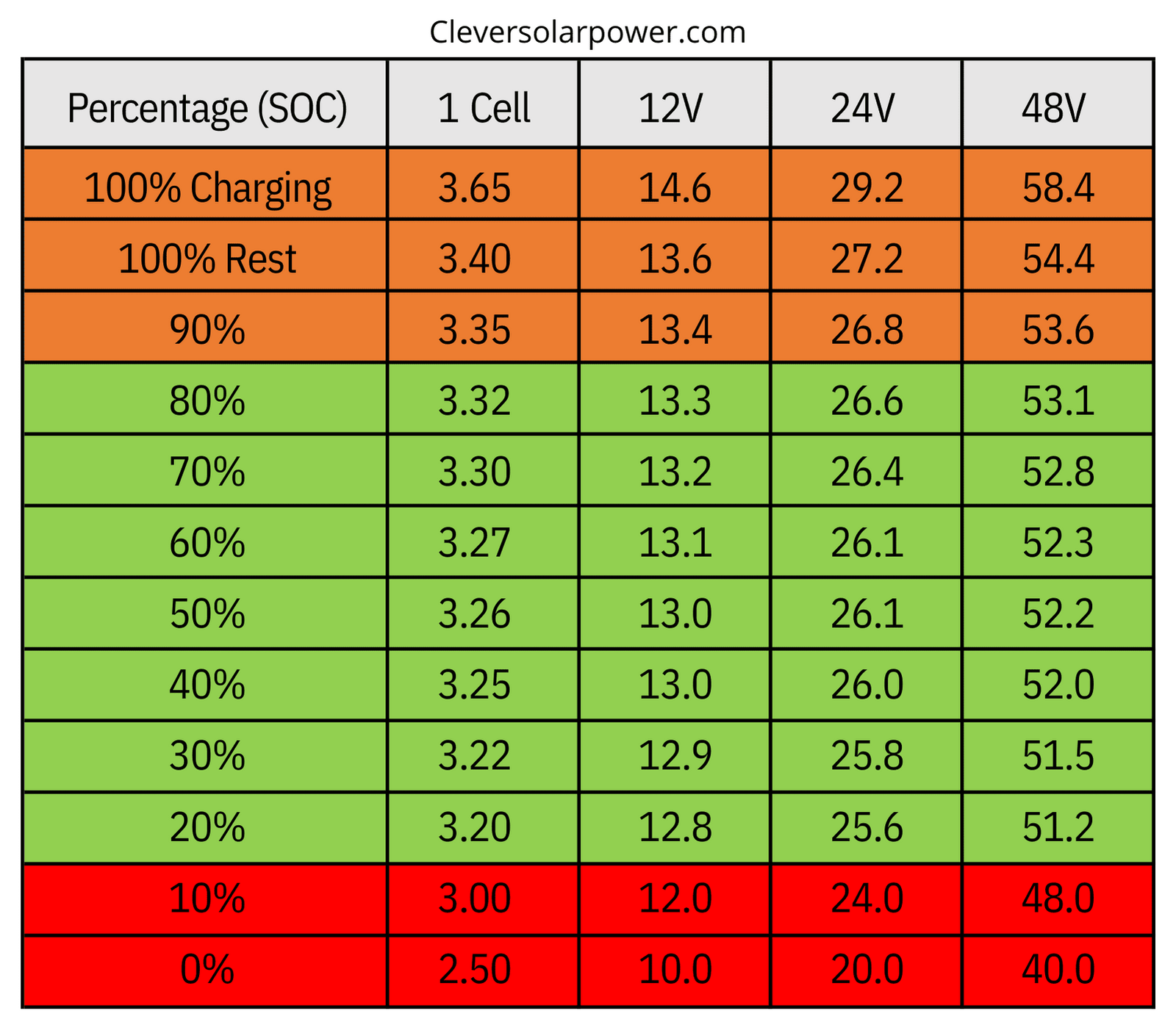
Generally speaking, LFP batteries thrive in moderate temperatures, typically between 15C and 35C (59F and 95F). This is their "happy place." Within this range, the electrochemical processes that generate power occur most efficiently, minimizing stress on the battery's internal components.
While that's the ideal range, LFP batteries are more resilient than some other types of lithium-ion. They can often operate somewhat outside of this ideal window without immediate catastrophic failure. However, prolonged exposure to temperatures outside the 15C to 35C range will contribute to accelerated degradation over time.
Think of it as consistently running a marathon. You can do it, but it's going to take a toll on your body over time. Similarly, consistently exposing an LFP battery to extreme temperatures, even if it still "works," will shorten its overall lifespan and diminish its performance.
The closer you can keep your LFP battery to that sweet spot — the Goldilocks zone, if you will — the longer it will last. It's like giving it a comfortable retirement package from day one! So, let's look at what happens when things get too hot or too cold.

Heat's Impact
3. The Effects of High Temperatures on LFP Batteries
High temperatures are a significant enemy of LFP batteries. When temperatures climb, the rate of chemical reactions inside the battery increases. This can lead to several detrimental effects. First, it accelerates the decomposition of the electrolyte, the fluid that allows ions to move between the electrodes. Think of it as the battery's blood supply becoming contaminated.
Second, high temperatures promote the formation of a solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer on the anode. While a thin SEI layer is necessary for battery operation, excessive growth of this layer increases internal resistance, hindering ion flow and reducing the battery's capacity to store and deliver energy. It's like plaque building up in your arteries, restricting blood flow.
Furthermore, extreme heat can cause structural changes within the battery electrodes, such as the breakdown of the LFP material itself. This irreversible damage reduces the number of active lithium ions available, further diminishing the battery's capacity and power output. Its similar to brick breaking down in a building over time.
The higher the temperature and the longer the exposure, the more pronounced these effects become. Repeated or prolonged exposure to high heat can significantly shorten an LFP battery's lifespan. So, finding ways to keep your battery cool, like proper ventilation or thermal management systems, is crucial.

What Is An LFP Battery And Does It Mean For EVs?
Cold Weather Concerns
4. The Impact of Low Temperatures on LFP Batteries
While LFP batteries are generally more tolerant of high temperatures than some other lithium-ion chemistries, cold weather presents its own set of challenges. At low temperatures, the internal resistance of the battery increases. This hinders the flow of ions and reduces the battery's ability to deliver power effectively. Imagine trying to run a marathon while wading through thick mud.
Furthermore, the electrochemical reactions within the battery slow down significantly at low temperatures. This reduces the battery's capacity and its ability to accept a charge. You might notice that your LFP battery charges much slower in cold weather, or that it doesn't hold as much charge as it does in warmer conditions.
In extreme cold, the electrolyte can become more viscous, further hindering ion transport. This can lead to a significant drop in performance and even potentially cause permanent damage if the battery is subjected to high discharge rates while frozen. Thats akin to blood thickening in cold weather, impacting circulation.
Although LFP batteries dont suffer from lithium plating to the same extent as some other lithium-ion batteries, very low temperatures can still promote this phenomenon, further reducing capacity and accelerating degradation. Strategies like pre-heating the battery before use in cold environments can help mitigate these issues and maintain optimal performance. Think of it as warming up before exercising in the cold.
Model 3 SR+ LFP Battery Range, Degradation, Etc Discussion Page 23
Mitigating Temperature Effects
5. Protecting Your LFP Batteries from Extreme Temperatures
So, what can you do to protect your LFP batteries from the harmful effects of temperature? Here are a few best practices:
Thermal Management Systems: If you're using LFP batteries in applications where temperature fluctuations are common, consider using a thermal management system. These systems can actively cool the battery in hot environments and heat it in cold environments, maintaining a more consistent operating temperature.
Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around your LFP batteries to prevent heat buildup. This is especially important in enclosed spaces or during charging and discharging.
Avoid Direct Sunlight: Don't leave LFP batteries in direct sunlight, as this can cause them to overheat. Store them in a cool, shaded area.
Controlled Charging: Use a charger specifically designed for LFP batteries and follow the manufacturer's recommendations for charging temperature. Avoid charging batteries in extreme temperatures.
Insulation: In cold environments, insulate your LFP batteries to help retain heat and prevent them from getting too cold.By implementing these strategies, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your LFP batteries and ensure reliable performance in a wide range of conditions. A little preventative maintenance goes a long way!
FAQ
6. Your Questions Answered
Let's address some common questions about LFP battery temperature and degradation.
Q: At what temperature does LFP battery degradation become significant?A: While some degradation occurs outside the 15C to 35C (59F to 95F) range, significant and accelerated degradation typically begins to occur at temperatures above 45C (113F) and below 0C (32F). Prolonged exposure to these extremes will shorten the battery's lifespan considerably.
Q: Can I charge an LFP battery below freezing?A: It's generally not recommended. Charging LFP batteries below 0C (32F) can cause lithium plating, which can permanently damage the battery. Some batteries have built-in heaters to prevent this. Always check the manufacturer's specifications.
Q: Does discharging an LFP battery in cold temperatures damage it?A: Discharging in cold temperatures reduces performance, but it's generally less harmful than charging. However, extremely low temperatures and high discharge rates can still cause stress. Consider pre-heating the battery if possible.
Q: How can I tell if my LFP battery has degraded due to temperature?A: Common signs of temperature-related degradation include reduced capacity (the battery doesn't hold as much charge), decreased power output (the battery can't deliver as much current), increased internal resistance (the battery heats up more quickly), and a shorter overall lifespan.